Secured vs Unsecured Loans Key Differences
Understand the fundamental differences between secured and unsecured loans and which is right for your needs.
Understand the fundamental differences between secured and unsecured loans and which is right for your needs. Navigating the world of loans can feel like deciphering a complex code, especially when terms like 'secured' and 'unsecured' are thrown around. But don't worry, it's not as complicated as it sounds. Essentially, the main difference boils down to whether you're putting up collateral to guarantee the loan. This distinction has a huge impact on everything from interest rates and approval odds to the potential risks you face. Let's dive deep into what makes these two types of loans tick, who they're best suited for, and some specific products you might encounter.
What Are Secured Loans Understanding Collateral and Risk
Alright, let's kick things off with secured loans. Think of a secured loan as a deal where you promise something valuable to the lender as a kind of insurance policy. This 'something valuable' is called collateral. If, for some reason, you can't repay the loan, the lender has the right to take possession of that collateral to recover their money. This significantly reduces the risk for the lender, which often translates into better terms for you, the borrower.
Common Types of Collateral for Secured Loans
- Real Estate: This is a big one. When you take out a mortgage to buy a house, the house itself serves as the collateral. If you default, the bank can foreclose on your home.
- Vehicles: Auto loans are another classic example. The car you're buying acts as collateral. Miss too many payments, and the lender can repossess it.
- Savings Accounts or Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Some lenders offer 'secured personal loans' or 'CD-secured loans' where your own savings account or CD is held as collateral. This is a great option for building credit, as the risk to the lender is almost zero.
- Investment Accounts: In some cases, you can use stocks, bonds, or mutual funds as collateral for a loan.
- Other Valuables: Less common for traditional loans, but pawn shops operate entirely on the principle of secured loans, using jewelry, electronics, or other items as collateral.
Advantages of Secured Loans for Borrowers
- Lower Interest Rates: Because the lender's risk is lower, they can afford to offer more attractive interest rates. This can save you a significant amount of money over the life of the loan.
- Higher Borrowing Limits: With collateral backing the loan, lenders are often willing to lend larger sums of money.
- Easier Approval: If you have a less-than-perfect credit score, a secured loan might be your best bet for approval, as the collateral provides a safety net for the lender.
- Longer Repayment Terms: Secured loans, especially mortgages, often come with much longer repayment periods, making monthly payments more manageable.
Disadvantages and Risks of Secured Loans
- Risk of Losing Collateral: This is the big one. If you can't make your payments, you stand to lose the asset you put up as collateral. This can be devastating, especially if it's your home or car.
- Requires an Asset: You need to own something valuable to use as collateral in the first place, which isn't always an option for everyone.
- Longer Application Process: Because collateral needs to be appraised and legally secured, the application process for secured loans can sometimes be more involved and take longer.
What Are Unsecured Loans Understanding Creditworthiness and Trust
Now, let's flip the coin and talk about unsecured loans. Unlike their secured counterparts, unsecured loans don't require any collateral. The lender is essentially taking a gamble on your promise to repay the loan. Their decision to lend to you is based almost entirely on your creditworthiness – your financial history, income, and overall ability to manage debt. This means your credit score and credit report play a much more critical role in getting approved for an unsecured loan.
Common Types of Unsecured Loans and Their Uses
- Personal Loans: These are often used for a wide variety of purposes, like consolidating high-interest debt, financing a wedding, covering unexpected medical expenses, or making home improvements.
- Credit Cards: Every time you swipe your credit card, you're essentially taking out a small, short-term unsecured loan. The credit limit is based on your creditworthiness.
- Student Loans: While some student loans can be federal and have different rules, many private student loans are unsecured, relying on your future earning potential.
- Lines of Credit: Similar to credit cards, a line of credit gives you access to a certain amount of money that you can draw from as needed, without collateral.
- Payday Loans: These are short-term, high-interest unsecured loans, often seen as a last resort due to their exorbitant fees. We'll touch on why these are generally a bad idea later.
Advantages of Unsecured Loans for Borrowers
- No Collateral Required: This is the most obvious benefit. You don't have to risk losing any of your assets.
- Faster Approval Process: Without the need to appraise collateral, unsecured loans often have a quicker application and approval process.
- More Flexible Use of Funds: Personal loans, in particular, often come with no restrictions on how you use the money.
Disadvantages and Risks of Unsecured Loans
- Higher Interest Rates: Because the lender is taking on more risk, they typically charge higher interest rates to compensate.
- Stricter Approval Requirements: You'll generally need a good to excellent credit score and a stable income to qualify for the best unsecured loan terms.
- Lower Borrowing Limits: Lenders are usually more conservative with the amounts they're willing to lend without collateral.
- Impact on Credit Score: While not a direct risk of losing an asset, defaulting on an unsecured loan will severely damage your credit score, making it difficult to borrow in the future. Lenders can also pursue legal action to collect the debt.
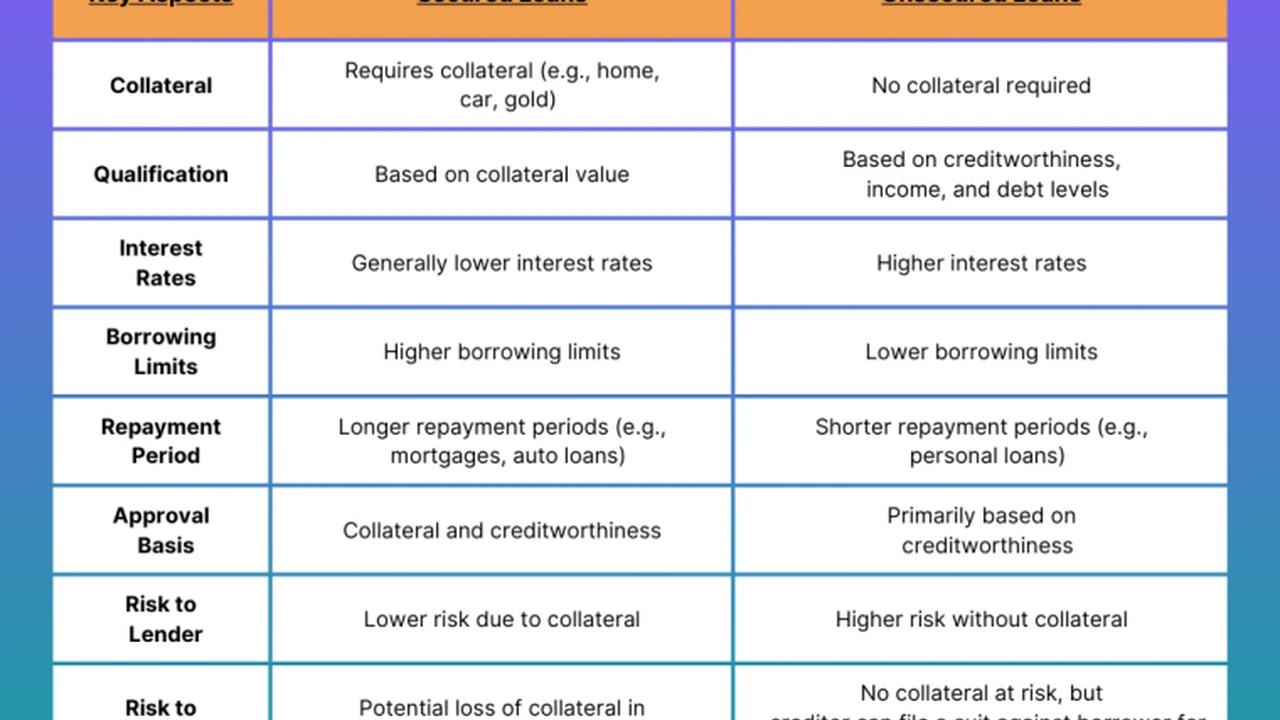
Secured vs Unsecured Loans A Side-by-Side Comparison
Let's put it all together in a quick comparison to really highlight the differences:
| Feature | Secured Loan | Unsecured Loan |
|---|---|---|
| Collateral Required? | Yes | No |
| Lender Risk | Lower | Higher |
| Interest Rates | Typically Lower | Typically Higher |
| Approval Odds | Easier, even with fair credit | Harder, requires good credit |
| Borrowing Limits | Higher | Lower |
| Repayment Terms | Can be longer | Generally shorter |
| Risk to Borrower | Loss of collateral | Damage to credit, legal action |
| Common Examples | Mortgages, Auto Loans, Secured Personal Loans | Personal Loans, Credit Cards, Student Loans |
Choosing the Right Loan for Your Financial Needs and Credit Score
So, how do you decide which type of loan is right for you? It really boils down to your specific situation, your credit score, and what you're comfortable risking.
When a Secured Loan Might Be Your Best Option
- You have a lower credit score: If your credit isn't stellar, a secured loan can be your ticket to getting approved, especially if you need a significant amount of money.
- You want lower interest rates: If you have valuable collateral and want to save money on interest, a secured loan is often the way to go.
- You're making a large purchase: For big-ticket items like a house or a car, secured loans are the standard and often the only practical option.
- You're trying to build credit: Secured credit cards or secured personal loans (backed by your own savings) are excellent tools for establishing or rebuilding a positive credit history.
When an Unsecured Loan Makes More Sense
- You have excellent credit: If your credit score is high, you'll likely qualify for competitive interest rates on unsecured loans, making them a convenient option without risking assets.
- You don't have collateral: If you don't own a valuable asset to put up, an unsecured loan is your only choice for borrowing.
- You need funds quickly for a smaller amount: For smaller, immediate needs, an unsecured personal loan can be approved and disbursed much faster than a secured loan.
- You prefer not to risk your assets: If the thought of losing your home or car keeps you up at night, an unsecured loan, despite potentially higher interest, offers peace of mind.
Specific Product Recommendations and Comparisons for Secured and Unsecured Loans
Let's look at some real-world examples and compare specific products you might encounter in the US and Southeast Asian markets. Keep in mind that interest rates and terms are highly variable based on your credit score, income, and the prevailing economic conditions.
Secured Loan Products and Their Applications
1. Auto Loans (Secured)
- Description: Loans specifically for purchasing a vehicle, with the car itself serving as collateral.
- Typical Use Case: Buying a new or used car.
- Pros: Generally lower interest rates than personal loans, longer repayment terms (up to 7 years), easier approval.
- Cons: Risk of repossession if you default.
- Example Lenders (US): Capital One Auto Finance, Chase Auto, local credit unions.
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia - e.g., Singapore/Malaysia): DBS Bank, Maybank, OCBC Bank.
- Comparison:
- Capital One Auto Finance (US): Offers pre-qualification without impacting your credit score, competitive rates for various credit tiers. Rates can range from 3% to 20% depending on credit.
- DBS Car Loan (Singapore): Often features attractive promotional rates, quick approval. Rates typically start around 2.78% p.a. for new cars.
- Pricing/Rates: Varies widely based on credit score, loan term, and vehicle age. Expect 3-10% for good credit, higher for fair credit.
2. Secured Personal Loans (Backed by Savings/CDs)
- Description: A loan where your own savings account or Certificate of Deposit (CD) is held as collateral. The loan amount is typically a percentage of your collateral.
- Typical Use Case: Building or rebuilding credit, getting a lower interest rate than an unsecured personal loan, or accessing funds without touching your savings directly.
- Pros: Very low interest rates, almost guaranteed approval, excellent for credit building, no risk of losing an external asset.
- Cons: You need to have savings to use as collateral, funds are tied up until the loan is repaid.
- Example Lenders (US): Navy Federal Credit Union, PNC Bank, local credit unions.
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia): Less common as a standalone product, but some banks might offer similar 'pledge loans' against fixed deposits.
- Comparison:
- Navy Federal Credit Union (US): Offers 'Pledge Loans' with rates as low as 2.00% APR, allowing you to borrow against your savings.
- PNC Bank (US): Offers 'Savings Secured Loans' with competitive rates, often just a few percentage points above the savings account interest rate.
- Pricing/Rates: Often very low, sometimes just 2-3% above the rate your savings account earns.
3. Secured Credit Cards
- Description: A credit card that requires a cash deposit, which then becomes your credit limit. This deposit acts as collateral.
- Typical Use Case: Building credit from scratch, rebuilding credit after financial difficulties.
- Pros: Easy to get approved, reports to credit bureaus (helping build credit), teaches responsible credit habits.
- Cons: Requires an upfront deposit, often has annual fees, may have higher APRs than traditional cards (though you should aim to pay in full).
- Example Lenders (US): Discover it Secured, Capital One Platinum Secured, Chime Credit Builder (unique, no hard credit check).
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia - e.g., Philippines/Indonesia): BDO Secured Credit Card, BPI Secured Credit Card (Philippines), Bank Mandiri (Indonesia).
- Comparison:
- Discover it Secured (US): No annual fee, earns cash back rewards (rare for secured cards), graduates to an unsecured card with good behavior. Deposit from $200.
- Capital One Platinum Secured (US): No annual fee, flexible deposit options (e.g., $49, $99, or $200 for a $200 limit), also reports to all three major bureaus.
- BDO Secured Credit Card (Philippines): Requires a hold-out deposit, often used by those without a credit history. Deposit from PHP 10,000.
- Pricing/Fees: Annual fees can range from $0 to $39. APRs typically 20-25%, but you should pay in full to avoid interest.
Unsecured Loan Products and Their Applications
1. Personal Loans (Unsecured)
- Description: A lump sum of money borrowed from a bank, credit union, or online lender, repaid in fixed monthly installments over a set period. No collateral required.
- Typical Use Case: Debt consolidation, home improvements, medical bills, wedding expenses, large purchases.
- Pros: No collateral risk, fixed payments, predictable repayment schedule, can be used for almost anything.
- Cons: Requires good to excellent credit for the best rates, higher interest rates than secured loans, lower borrowing limits.
- Example Lenders (US): SoFi, LightStream, Marcus by Goldman Sachs, Upgrade.
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia - e.g., Thailand/Vietnam): SCB (Siam Commercial Bank), Kasikornbank (Thailand), VPBank (Vietnam).
- Comparison:
- SoFi (US): Known for competitive rates for borrowers with excellent credit, no origination fees, unemployment protection. Rates from 8.99% to 29.99% APR.
- LightStream (US): Offers very low rates for top-tier credit, but requires excellent credit. Rates from 6.99% to 23.99% APR.
- SCB Personal Loan (Thailand): Offers various personal loan products, often with quick approval for eligible customers. Rates can be around 10-25% p.a.
- Pricing/Rates: For excellent credit, rates can start around 6-8% APR. For fair credit, expect 15-30% APR. Origination fees (1-8%) may apply.
2. Credit Cards (Unsecured)
- Description: A revolving line of credit that allows you to borrow money up to a certain limit, repay it, and borrow again.
- Typical Use Case: Everyday purchases, emergency expenses, earning rewards (cash back, travel points), building credit (when used responsibly).
- Pros: Convenience, rewards programs, fraud protection, can build credit quickly.
- Cons: High interest rates if balances are carried, easy to fall into debt, annual fees on some premium cards.
- Example Lenders (US): Chase Sapphire Preferred, American Express Gold, Citi Double Cash, Capital One Quicksilver.
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia): UOB One Card (Singapore), CIMB Platinum (Malaysia), BPI Blue Mastercard (Philippines).
- Comparison:
- Chase Sapphire Preferred (US): Excellent for travel rewards, sign-up bonus, annual fee $95. APR 21.49% - 28.49%.
- Citi Double Cash (US): 2% cash back on everything (1% when you buy, 1% when you pay), no annual fee. APR 19.24% - 29.24%.
- UOB One Card (Singapore): Offers high cash back for specific spending categories, often with minimum spend requirements. APR typically 26.9% p.a.
- Pricing/Fees: APRs typically range from 15% to 30%. Annual fees can be $0 to hundreds for premium cards.
3. Student Loans (Unsecured - Private)
- Description: Loans from private lenders to cover educational expenses, not backed by the government.
- Typical Use Case: Funding higher education when federal aid isn't enough.
- Pros: Can cover significant educational costs, often have deferment options while in school.
- Cons: Often require a co-signer if the student has limited credit, interest rates can be variable and higher than federal loans, limited repayment flexibility compared to federal loans.
- Example Lenders (US): Sallie Mae, Ascent, College Ave.
- Example Lenders (Southeast Asia): Many local banks offer education loans, e.g., Maybank Education Loan (Malaysia), BDO Education Loan (Philippines).
- Comparison:
- Sallie Mae (US): Offers various loan options for different degrees, competitive rates for good credit. Variable APR from 6.12% to 16.35%, Fixed APR from 4.25% to 15.49%.
- Ascent (US): Known for offering loans to students without a co-signer based on future earning potential. Variable APR from 6.23% to 16.07%, Fixed APR from 4.29% to 16.66%.
- Pricing/Rates: Highly dependent on credit score (and co-signer's credit), can range from 4% to 16% APR.
The Importance of Your Credit Score in Loan Applications
No matter if you're looking at secured or unsecured loans, your credit score is going to be a major player. For unsecured loans, it's practically the star of the show. A higher credit score tells lenders you're a responsible borrower, which means they're more likely to offer you lower interest rates and better terms. For secured loans, while collateral reduces the risk, a good credit score can still get you the absolute best rates available. It's always a good idea to check your credit score and report regularly and work on improving it if needed before applying for any significant loan.
Final Thoughts on Borrowing Responsibly
Understanding the difference between secured and unsecured loans is a fundamental step in smart financial decision-making. Both have their place, and the 'best' option really depends on your individual circumstances. Always consider the risks, especially with secured loans where your assets are on the line. For unsecured loans, be mindful of the higher interest rates and ensure you can comfortably meet the repayment schedule. Always shop around, compare offers from multiple lenders, and read the fine print before committing to any loan. Borrowing money can be a powerful tool to achieve your financial goals, but it requires careful planning and responsible management.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)






